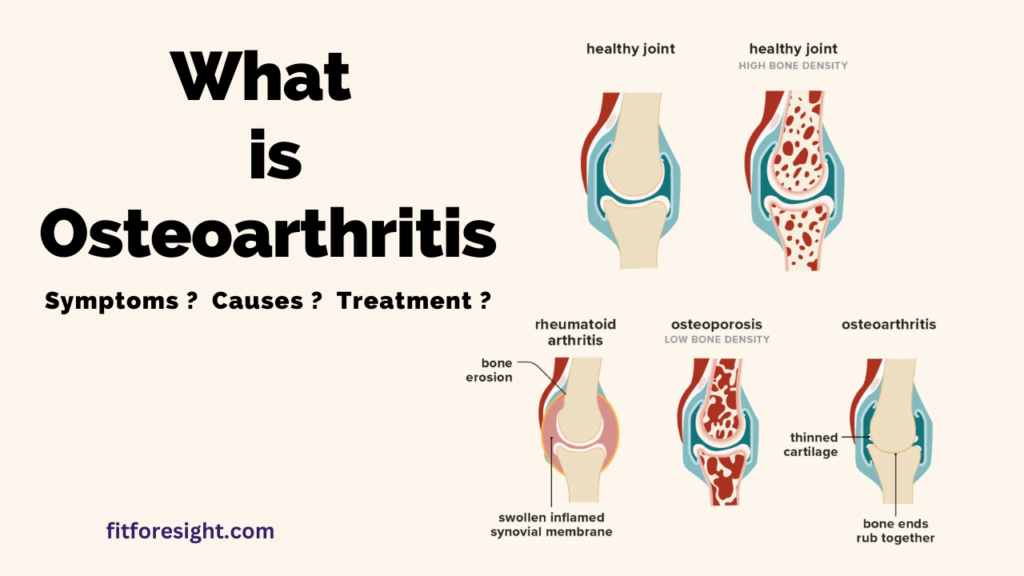
Osteoarthritis is a type of arthritis that is caused by the wear and tear of the protective cartilage that cushions the joints. This can lead to pain, stiffness, and swelling in the affected joints. Osteoarthritis is most common in the hands, hips, knees, and spine.
Symptoms of osteoarthritis can include:
- Symptoms of osteoarthritis can vary depending on the joint that is affected, but common symptoms of osteoarthritis include:
- Pain in the affected joint, which may worsen with movement or after prolonged periods of rest
- Stiffness in the affected joint, especially after sleeping or sitting for a long time
- Swelling or tenderness in the affected joint
- A crunching or grating sensation when the joint is moved
- Loss of flexibility or range of motion in the affected joint
- In some cases, osteoarthritis may cause no symptoms or only mild symptoms, but in severe cases, it can significantly impact a person’s quality of life. It’s important to see a healthcare provider if you experience any symptoms of osteoarthritis to receive an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
- Osteoarthritis causes
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease that occurs when the protective cartilage that cushions the ends of bones wears down over time. While the exact cause of osteoarthritis is not fully understood, there are several factors that are thought to contribute to its development. These include:
- Age: Osteoarthritis is more common in older adults, and as we age, the cartilage in our joints can start to break down.
- Obesity: Being overweight puts extra pressure on the joints, particularly the knees, hips, and spine, which can increase the risk of developing osteoarthritis.
- Joint injuries: Previous injuries or trauma to a joint can increase the risk of developing osteoarthritis in that joint.
- Genetics: There may be a genetic component to osteoarthritis, as some people may be more predisposed to developing the condition due to inherited factors.
- Repetitive stress: Repetitive stress on a joint, such as from a job or hobby that involves frequent use of a joint, can increase the risk of osteoarthritis in that joint.
- Other medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis, gout, or metabolic disorders, can increase the risk of developing osteoarthritis.
Overall, osteoarthritis is a complex condition that can have multiple contributing factors. By identifying and addressing these factors, it may be possible to reduce the risk of developing osteoarthritis or slow its progression.
Treatment of Osteoarthritis
The treatment of osteoarthritis typically focuses on managing symptoms and slowing the progression of the disease. The following are some common treatments for osteoarthritis:
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can help relieve pain and reduce inflammation. Stronger prescription pain relievers may also be prescribed for severe pain.
- Physical therapy: Physical therapy can help improve joint flexibility, strength, and mobility. This can include exercises to strengthen the muscles surrounding the affected joint and low-impact aerobic exercises, such as walking or swimming.
- Weight management: Being overweight can put extra stress on weight-bearing joints, such as the knees and hips, which can exacerbate osteoarthritis symptoms. Weight loss can help reduce the stress on the joints and improve symptoms.
- Assistive devices: Devices such as braces, splints, or canes can help support and stabilize the affected joint, reducing pain and improving mobility.
- Injections: Corticosteroid injections or hyaluronic acid injections can be used to reduce inflammation and relieve pain in the affected joint.
- Surgery: Joint replacement surgery may be necessary in severe cases of osteoarthritis, such as when the joint is severely damaged and causing significant pain and mobility issues.
It’s important to work with a healthcare provider to develop an individualized treatment plan for osteoarthritis based on your specific symptoms and needs. Treatment may involve a combination of approaches to effectively manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
See Video
View Comments (2)
Hi. Gracias for the great articleread! Lovelike to read more about this subject!
Thank You Dear .